One of the most prevalent abnormal heartbeats is atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib). When the heart beats too slowly or too quickly, it has an arrhythmia.
Blood does not properly flow from the top chambers of the heart to the lower chambers when there is atrial fibrillation. A persistent disease or short bouts of atrial fibrillation are also possible.
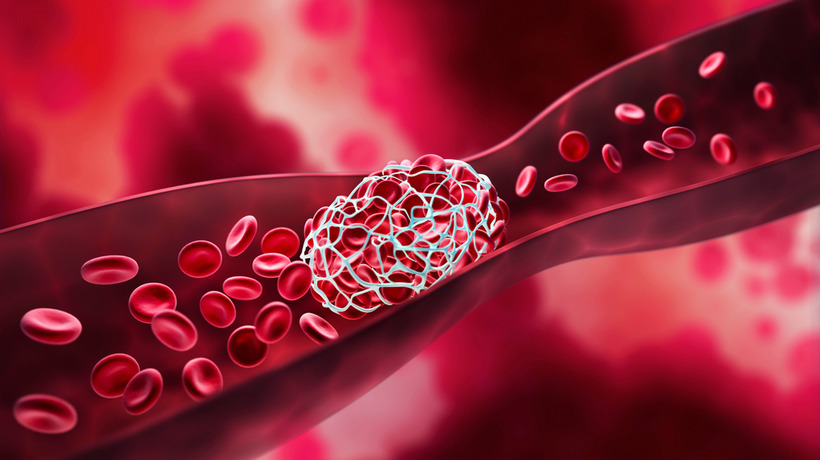
Future issues like a blood clot, which can result in a stroke or create a pulmonary embolism, could be caused by atrial fibrillation. Additionally, it might weaken the heart and reduce the heart’s capacity to pump blood.
The likelihood of getting atrial fibrillation is increased in older adults. Atrial fibrillation risk is also higher in people with high blood pressure, thyroid conditions, and obesity. Alcohol can cause an atrial fibrillation event in some people, and excessive drinking raises the risk even more.
Signs of atrial fibrillation
The Cleveland Clinic lists the following as the most typical indications of atrial fibrillation:
- Heart palpitations, sudden pounding, fluttering or racing sensation in the chest
- Lack of energy or feeling over-tired
- Dizziness or feeling light-headed
- Pain, pressure or discomfort in the chest
- Shortness of breath, having difficulty breathing during normal activities and even at rest








